Assessment of the economic impact of restrictive government policies (lockdowns) to combat coronavirus

According to assessment, GDP loses (direct, indirect and induced) due to restrictive government policies (lockdowns) to contain spread of the virus over the world amounted over 250 billion USD per each working day or 0.3% of global GDP.
Assessment approach and general assumptions
The assessment based on very simple approach. Direct loses of the GDP calculated based on number of employees in lockdowns (restricted from the work or imposed non-working days) multiplied by labor productivity (GDP per employed). In its turn number of employees in lockdowns calculated based on number of population under restrictions and employment to population ratios. Employment to population ratios adjusted to take into account usual exemptions, such as public utilities, groceries, food production, health care providers, pharmaceutical and other related producers and service providers, etc. In base scenario employment to population ratios reduced by 10 percentage points to reflect exclusions from lockdowns.
In addition to direct effects and more harmful will be various indirect and induced loses resulted from (i) reduced internal demand down the supply chain; (ii) reduced internal demand induced by reduced incomes of households; (iii) reduced external demand induced by reduced outputs of counterpart countries (iv) reduced external demand resulted from travel bans; (v) reduced external demand resulted from cargo interruptions, etc. Putting in simple words, if as a result of lockdowns and isolations, people cannot produce something then those not under this restriction can end up with luck of supplies or/and luck of demand for their goods and services, so called multiplier effects. The basic, somehow trivial observation, is that if, for example 30% of economy is shut down for one day due to restrictions, then overall economic losses will be in a range of 30% to 100% of the daily GDP of the economy[1], depending on magnitude of economic integration. In this example indirect and induced losses can be in the range of 1 to 3. At this point it is important to note that in case that restrictions applied entirely to economy then there is no multiplier effect in place and the loss will be just the 100% of GDP otherwise have been produced in that particular period of time.
Main assumptions are as follows:
Multiplier (which includes direct, indirect and induced effects) is calculated by dividing total employment to estimated employment in lockdown and divided by 2
Employment ratio in lockdown calculated by subtracting 10 percentage point from employment to population ratio
Finally as both of main indicators: employees in lockdown and GDP multiplier are most sensitive and based on ambiguous assumptions. Sensitivity analysis in respect of these two indicators presented for each assessment.
Assessment results
World
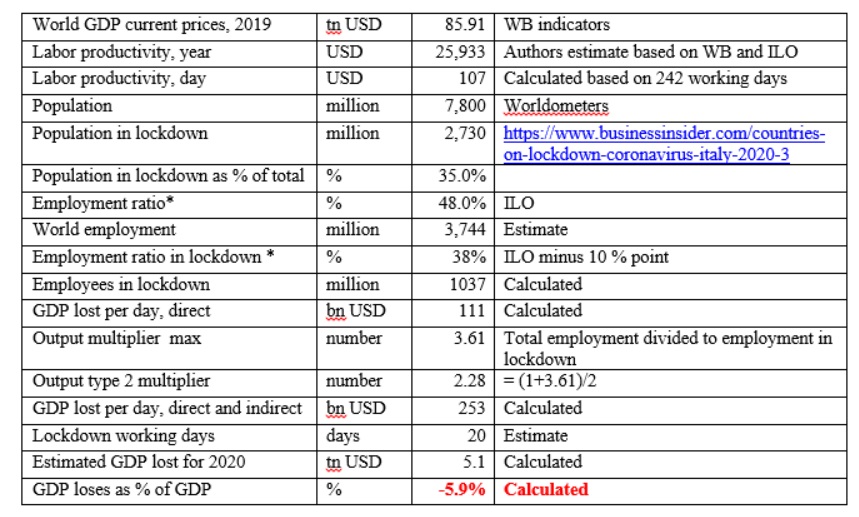
Sensitivity analysis in respect of GDP multiplier and Employment ratio presented in the table below.

For assessment of the coronavirus containment measures direct impact on Armenia economy two additional assumptions has been used. First, as agriculture output in Armenia predominantly produced in small, family based farms, labor productivity and employment in lockdown does not include agriculture. Second, since 2018 there are different statistics on employment, two main are Labor force survey and State revenue committee data base. The assessment use labor force survey statistics according which employment to population ration in Armenia without agricultural employment amount to 780 thousands or 26% of population.
Armenia
Armenia economy has one important characteristic which make it more vulnerable to external shocks originated in Russia In addition to the assessment of economic impact of the internal lockdown and isolation measures, in Armenia case, it is important also to evaluate coronavirus impact on remittances. Remittances, from working migrants and private transfers, originated predominantly from Russia and amount to about 9% (in net terms) of the Armenia GDP. As both Russia and Armenia impose travel bans most vulnerable will be situation with working migrants. In 2018 net primary incomes from working migrants amount to 657 million USD. We estimate that the travel restrictions main remain in place for 120 days and taking into account induced losses the total GDP loss will amount to 280 million USD for 2020. In respect of private transfers ( 490 million USD) main losses for Armenia economy will be as a result of depreciation of Russian ruble and reduced population incomes due to coronavirus impact.
The main assumptions and calculations for the Armenia economy presented in Table 2.
Table 2 COVID19 economic impact assessment results, Armenia

Sensitivity analysis in respect of GDP multiplier and Employment ratio presented in the table below.

inecbus.rau.am

























